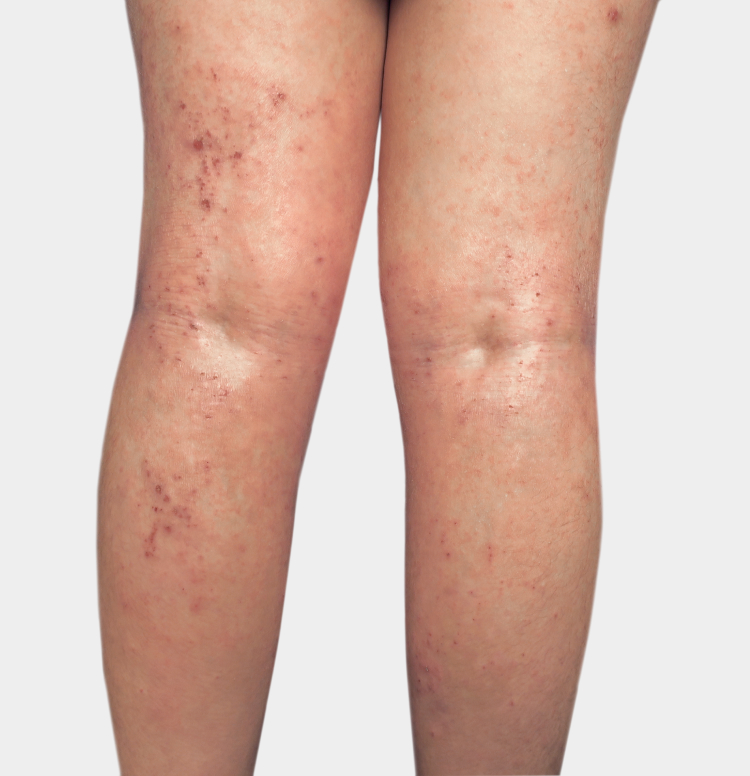
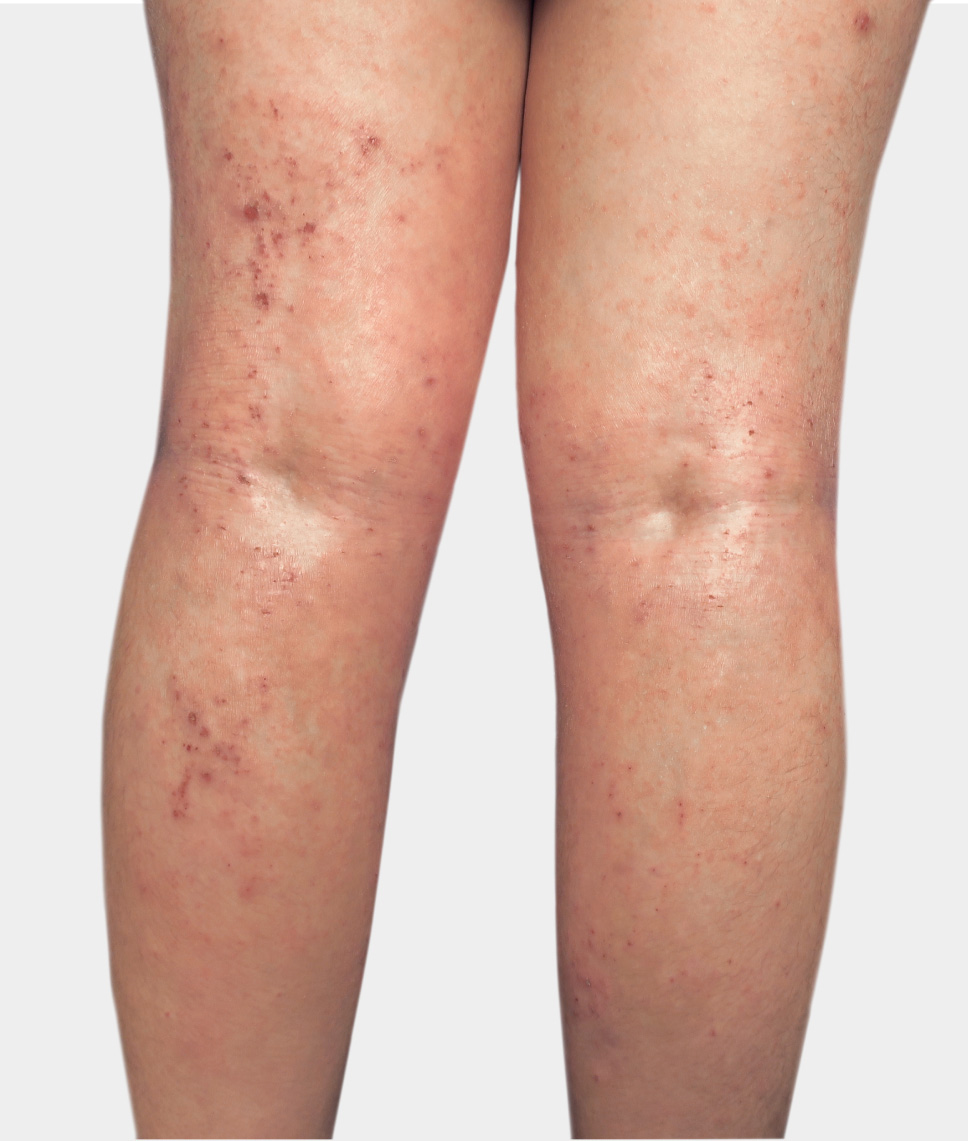
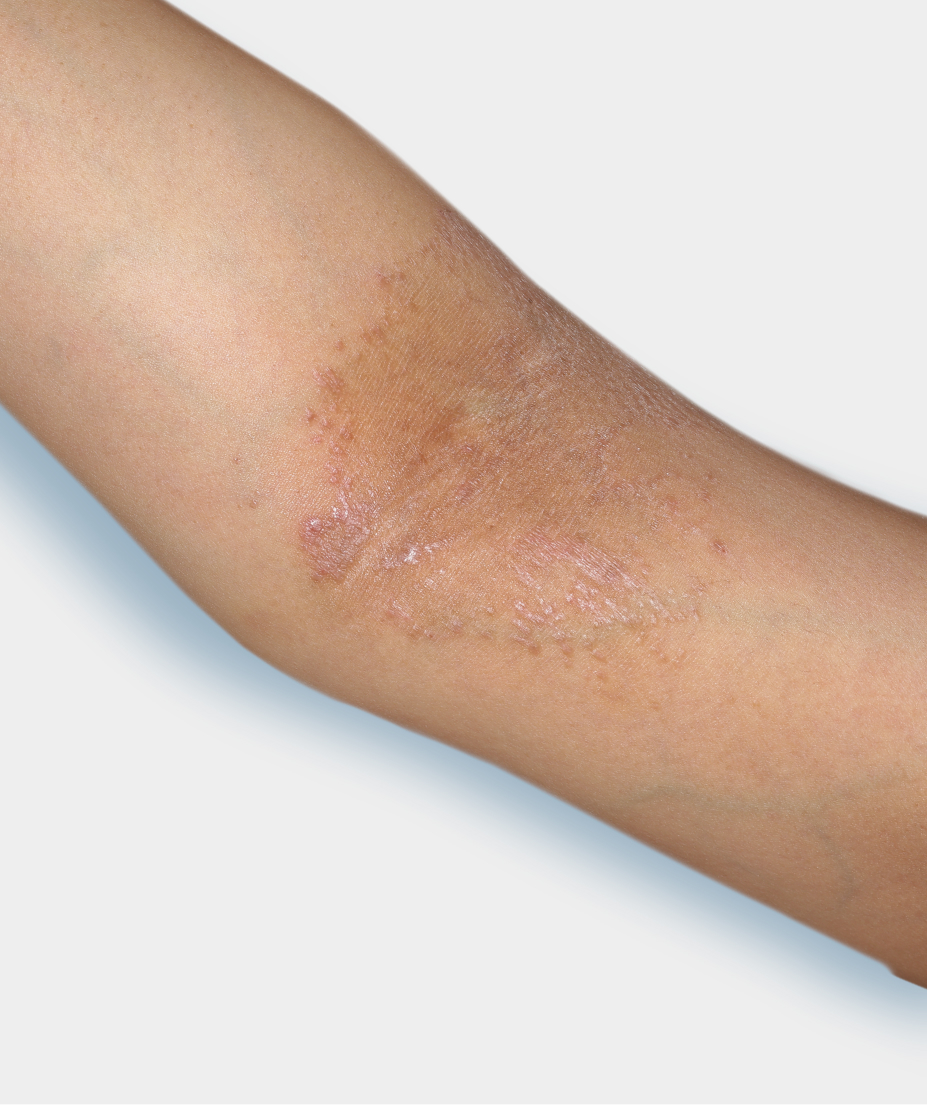
Individual results may vary.
Patient Identification
Appropriate patients may
benefit from seeing a
dermatologist or allergist
The latest American Academy of Dermatology treatment guidelines for the management of moderate-to-severe atopic
dermatitis in appropriate adults include a strong recommendation for the use of systemic therapies,
such as DUPIXENT1

-
Have tried a variety of topical prescription therapies for moderate-to-severe
atopic dermatitis and are still uncontrolled1-3 - Suffer from inadequate control of pruritus1
-
Have moderate-to-severe erythema and moderate-to-severe
papulation/
infiltration (IGA 3 or 4)2 - Have >10% of their body covered with lesions1
- Have disease that may involve problem areas, such as the face, hands, and feet1

- IGA, Investigator's Global Assessment
Atopic Dermatitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Dupixent is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
Bullous Pemphigoid: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with bullous pemphigoid (BP).
INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSHypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. A case of AGEP was reported in an adult subject who participated in the bullous pemphigoid development program. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD, COPD, and BP subjects who received DUPIXENT versus placebo, with conjunctivitis being the most frequently reported eye disorder in AD. Conjunctivitis also occurred more frequently in adult CRSwNP and PN subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis and keratitis have been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis. Advise patients or their caregivers to report new-onset or worsening eye symptoms. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program and cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD, acute bronchospasm, or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma: Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis: Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, these cases resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT. Advise patients to report new-onset or worsening joint symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:Most common adverse reactions are:
- Atopic Dermatitis (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia. The safety profile in pediatric patients through Week 16 was similar to that of adults with AD. In an open-label extension study, the long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in pediatric patients observed through Week 52 was consistent with that seen in adults with AD, with hand-foot-and-mouth disease and skin papilloma (incidence ≥2%) reported in patients 6 months to 5 years of age. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
- Asthma (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (incidence ≥1% in adult patients): injection site reactions, eosinophilia, insomnia, toothache, gastritis, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, arthralgia, and herpes viral infections.
- Prurigo Nodularis (incidence ≥2%): nasopharyngitis, conjunctivitis, herpes infection, dizziness, myalgia, and diarrhea.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (incidence ≥2%): viral infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, urinary tract infection, local administration reactions, rhinitis, eosinophilia, toothache, and gastritis.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions.
- Bullous Pemphigoid (incidence ≥2%): arthralgia, conjunctivitis, vision blurred, herpes viral infections, keratitis.
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1-877-311-8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information
Atopic Dermatitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Dupixent is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
Bullous Pemphigoid: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with bullous pemphigoid (BP).
INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSHypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. A case of AGEP was reported in an adult subject who participated in the bullous pemphigoid development program. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD, COPD, and BP subjects who received DUPIXENT versus placebo, with conjunctivitis being the most frequently reported eye disorder in AD. Conjunctivitis also occurred more frequently in adult CRSwNP and PN subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis and keratitis have been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis. Advise patients or their caregivers to report new-onset or worsening eye symptoms. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program and cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD, acute bronchospasm, or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma: Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis: Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, these cases resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT. Advise patients to report new-onset or worsening joint symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:Most common adverse reactions are:
- Atopic Dermatitis (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia. The safety profile in pediatric patients through Week 16 was similar to that of adults with AD. In an open-label extension study, the long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in pediatric patients observed through Week 52 was consistent with that seen in adults with AD, with hand-foot-and-mouth disease and skin papilloma (incidence ≥2%) reported in patients 6 months to 5 years of age. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
- Asthma (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (incidence ≥1% in adult patients): injection site reactions, eosinophilia, insomnia, toothache, gastritis, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, arthralgia, and herpes viral infections.
- Prurigo Nodularis (incidence ≥2%): nasopharyngitis, conjunctivitis, herpes infection, dizziness, myalgia, and diarrhea.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (incidence ≥2%): viral infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, urinary tract infection, local administration reactions, rhinitis, eosinophilia, toothache, and gastritis.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions.
- Bullous Pemphigoid (incidence ≥2%): arthralgia, conjunctivitis, vision blurred, herpes viral infections, keratitis.
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1-877-311-8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information